Biography
I am an applied forest ecologist, data science consultant, and Graduate Research Fellow in the Forest Geospatial Lab at Michigan State University.
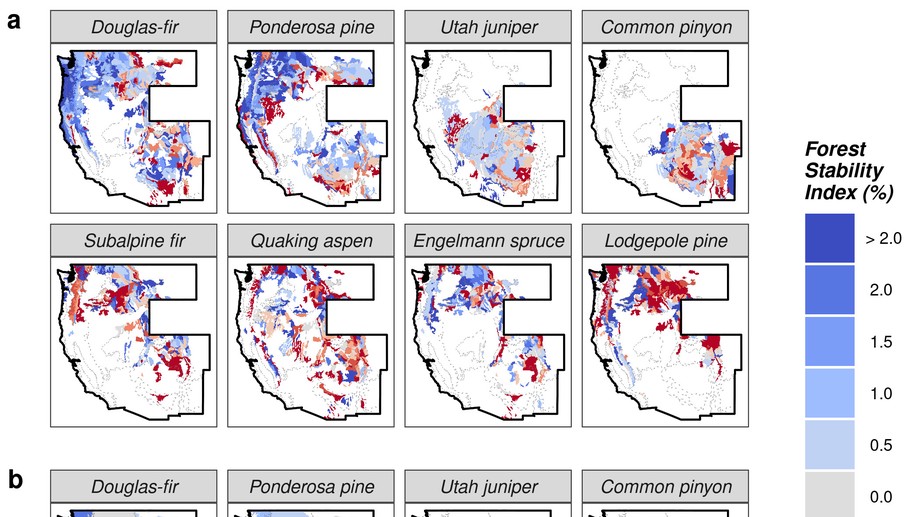
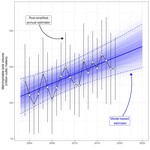
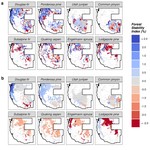
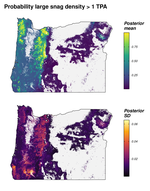
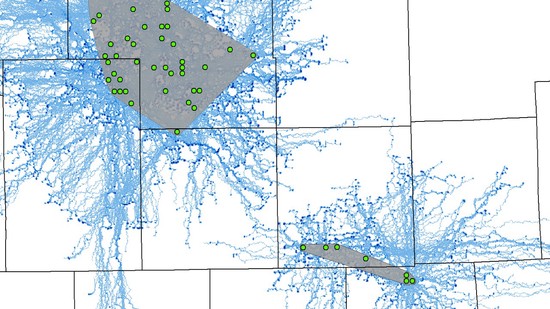
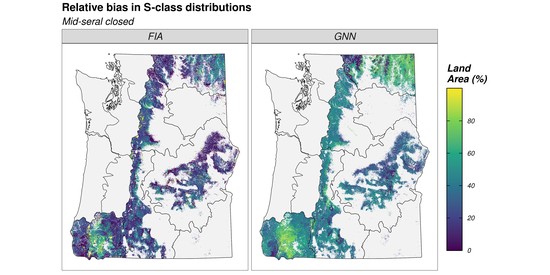
My research and consulting interests are generally structured around the integration of field studies, “big data”, and advanced statistics to solve pressing issues in forest management and ecology. My current work involves quantifying forest structural restoration needs in the Pacific Northwest, specifically detecting and attributing multidecadal changes in the “ecological departure” of forest landscapes in the region. I am also leading efforts to advance understanding of the consequences of disturbance, climate, and management legacies on temperate forest demography and biomass dynamics across multiple scales.
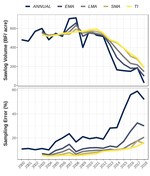
I am the lead author and maintainer of rFIA, an R package designed to increase the accessibility and use of the USFS Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) Database. Check out our website for more information, tutorials, and documentation on rFIA. You can also find us on CRAN and GitHub, and in a recent article in Environmental Modeling and Software. For bug reports or feature requests, please see our active issues page.
Interests
- Disturbance & Landscape Ecology
- Forest Management & Decision Science
- Quantitative Silviculture
- Conservation Finance & Impact Investing
Education
-
PhD Forestry
Michigan State Univeristy
-
PhD Environmental and Forest Science
Univeristy of Washington
-
MS Forestry, 2020
Michigan State Univeristy
-
BS Forestry, 2019
Michigan State University